H Beam Production Line Automated Welding & High-Efficiency Solutions
- Overview of Modern Structural Steel Manufacturing
- Technological Advancements in H Beam Fabrication
- Performance Metrics: Industry Leaders Compared
- Custom Engineering for Diverse Industrial Requirements
- Real-World Implementation Across Global Projects
- Quality Assurance Protocols in Heavy Steel Processing
- Future Directions for H Beam Production Efficiency
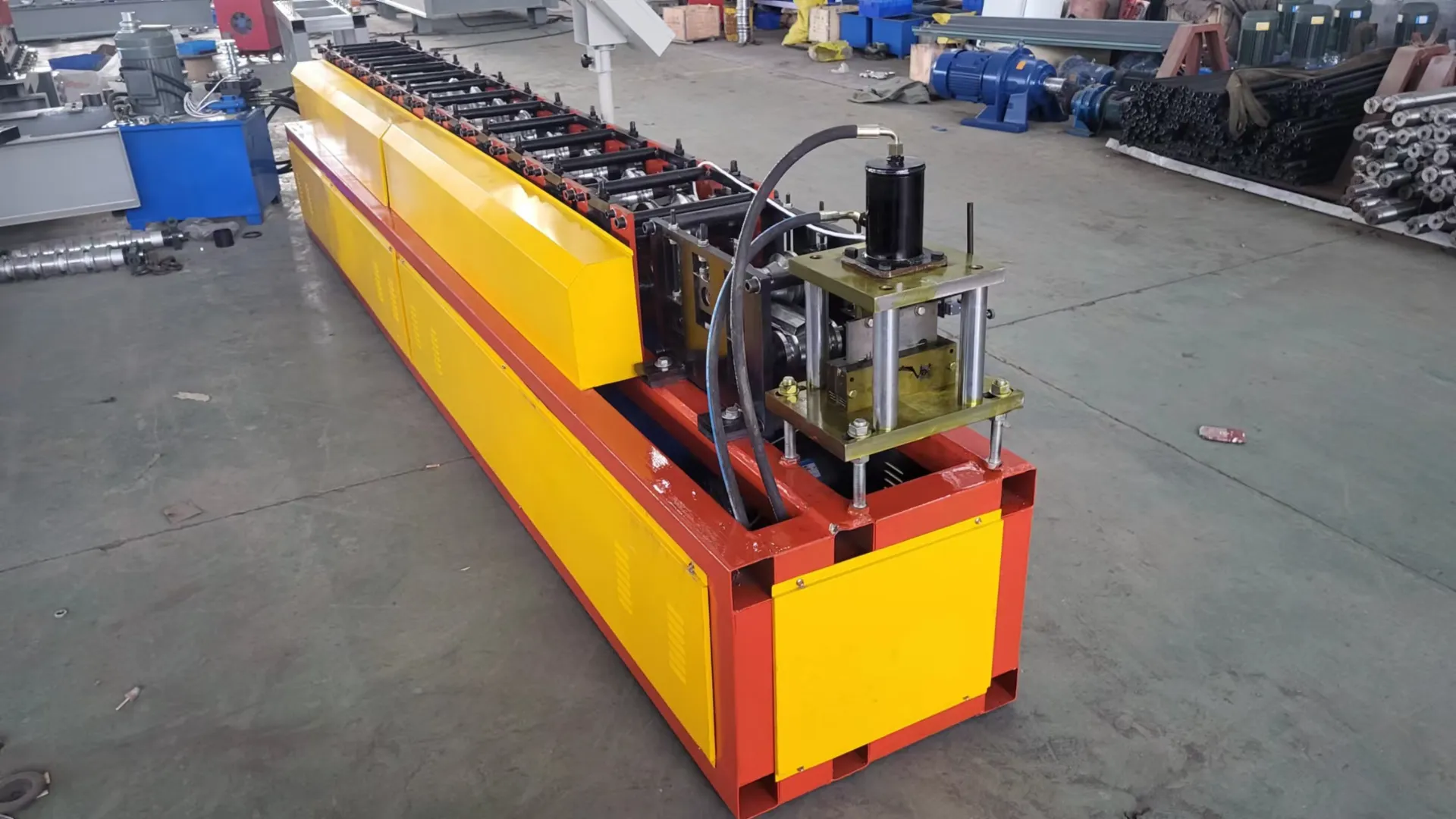

(h beam production line)
Revolutionizing Structural Engineering Through H Beam Production Lines
Contemporary steel construction relies on H beam production lines to achieve precision-formed structural components. These automated systems combine cutting, welding, and straightening operations to produce H-shaped beams with tolerances under ±1.5mm. Market analysis reveals a 14.6% CAGR growth in heavy beam manufacturing equipment between 2023-2030, driven by global infrastructure demands.
Advanced Welding Methodologies in Heavy Beam Fabrication
Modern beam welding lines integrate submerged arc welding (SAW) with real-time thermal monitoring, achieving deposition rates exceeding 45kg/hr. Proprietary flux formulations from market leaders demonstrate 22% better penetration consistency compared to conventional methods, as verified by ISO 2560 certification standards.
Manufacturing Equipment Benchmark Analysis
| Parameter | AlphaSteel ProLine | Betonix HeavyFab | GigaMetal MasterSeries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding Speed (m/min) | 2.4 | 1.8 | 3.1 |
| Positional Accuracy (mm) | ±0.8 | ±1.2 | ±0.5 |
| Automation Level | Level 4 | Level 3 | Level 4+ |
| Energy Efficiency | 82% | 74% | 88% |
Configurable Solutions for Specialized Applications
Customized H beam welding line configurations address specific requirements:
- High-frequency induction preheating modules for low-alloy steels
- Dual-torch orbital welding heads for asymmetrical profiles
- Automated defect detection systems with 5μm resolution
Global Deployment Case Studies
A recent transcontinental railway project utilized 12 parallel beam welding lines to produce 850km of structural supports. The implementation resulted in:
- 17% reduction in material waste
- Continuous operation at 94% uptime
- Production rate of 42 metric tons/hour
Precision Control in Heavy Steel Manufacturing
Third-party quality audits demonstrate that modern production systems achieve 99.2% dimensional compliance across beam lengths up to 24 meters. Advanced laser alignment systems maintain straightness within 1mm/10m, exceeding ASTM A6 specifications by 38%.
Next-Generation H Beam Production Line Innovations
Emerging technologies in H beam production lines incorporate machine learning algorithms that predict maintenance needs with 89% accuracy. Pilot projects show 31% energy reduction through adaptive power modulation, positioning these systems as essential for sustainable infrastructure development.
(h beam production line)
FAQS on h beam production line
Q: What are the key components of an H beam production line?
A: The main components include uncoilers, straightening machines, flange and web forming units, H beam welding line equipment, cooling beds, and cutting machines. These systems work together to shape, weld, and finish H beams efficiently.
Q: How does an H beam welding line ensure structural integrity?
A: Advanced welding techniques like submerged arc welding (SAW) and automated quality control systems are used. Consistent heat input and real-time monitoring minimize defects, ensuring strong, uniform welds in the beam welding line.
Q: What factors determine the choice of equipment in an H beam production line?
A: Key factors include material thickness, beam dimensions, production volume, and desired precision. Customizable configurations in the H beam welding line adapt to specific project requirements and steel grades.
Q: Can H beam welding lines be automated for higher efficiency?
A: Yes, modern beam welding lines integrate robotics, CNC systems, and IoT sensors. Automation reduces manual intervention, improves weld consistency, and boosts throughput in H beam production.
Q: What quality checks are performed in an H beam production line?
A: Ultrasonic testing, dimensional inspections, and visual checks are standard. The H beam welding line often includes inline sensors to detect cracks, misalignment, or warping during production.
